Graham Reid | | 2 min read

When the English author Thomas DeQuincey was describing nightmarish drug-induced visions in his early-19th-century autobiography Confessions of an English Opium Eater, he reflected on curious and compelling images he had never seen.
They were a set of engravings by Italian artist Giovanni Battista Piranesi, and DeQuincey referred to descriptions of them by his fellow author and opium-aficionado, the poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge.
DeQuincey described the plates as full of vast Gothic halls with enormous pulleys and levers, massively oppressive walls, and shadowy staircases which led to nowhere other than a dark abyss.
They were disturbing opiate-inspired visions - and DeQuincey mistakenly referred to them as Piranesi's Dreams. His error, given their content and his emotionally heightened - if occasionally addled - frame of mind, is forgivable.
But they were Piranesi's I Carceri/Prisons series which came in two editions, the second 16 years after the first and a darker, more discomforting vision.
DeQuincey was moved enough to write about them through a second-hand account.
Piranesi (1720-1778) is often described as an engraver of architecture, but that description is inadequate and prosaic. Certainly his works are predominantly of architecture, and specifically that of ancient and post-classical Baroque Rome.
But his works are of such internal scale and grandeur that they imprint themselves in the imagination. His ancient world is usually rendered as massive, oppressive and humbling to Man. What people there are in his works - and there are few, often none - are there as tiny figures peeping about among the ruins.
As John Ford's films set in Monument Valley defined "the West" for cinema audiences in the middle of last century, so Piranesi's etchings of Rome shaped the way his contemporaries - and people for at least a generation subsequent - viewed the Rome they saw on their Grand Tour.
Piranesi's work also shaped the Neoclassical Movement and the Romantic imagination of William Wordsworth, Coleridge and, of course, DeQuincey.
We, too, have inherited the legacy. Today, a set designer given the brief "prison, dark, oppressive" would most likely refer to Piranesi's overpowering visions. There are scenes in the first Hellboy film which directly draw on I Carceri.
Venice-born Piranesi was a trained architect and stonemason, but his etchings leap from the literal into the realm of the imagination.
At 20 he went to Rome as a draughtsman for the Venetian ambassador and studied printmaking. His innovative techniques of multiple scoring of acid into a plate allowed for stark contrasts, from shafts of light through penumbra into deep, foreboding and dramatic darkness.
The I Carceri series - the first edition completed a few years after arriving in the city of his childhood dreams - are his most powerful and memorable works.
In subsequent projects he turned his attention to the living Rome he saw around him: the great Baroque palaces, the tombs and triumphal arches.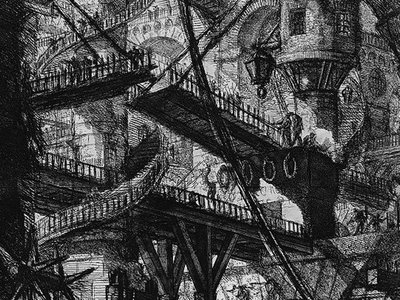
Piranesi produced around 2000 plates in his lifetime and they were bought by tourists to Rome in his day much as visitors now will snap up postcards and large photo-spread books of the Colosseum and Forum.
Piranesi's works - particularly his Grotteschi and I Carceri series - were the Rome of his invention, a theatrical exaggeration which imprinted itself on those who saw them or, as in DeQuincey's case, just heard about them second-hand.
He still shapes the contemporary imagination's image of Roman ruins. Piranesi wrote an autobiography, which is regrettably lost to us. However, one of his sons published a brief account of his father's career.
One passage stands out as a summation of this influential artist's work, which wove together the ancient and contemporary, the real and the fanciful.
"In an age of frivolities, he boldly and single-handedly dared to strike out for himself on a new road to fame: and in dedicating his talent to the recording and illustrating from ancient writers of the records of former times, he met with a success as great as it deserved, combining, as it did, all that was beautiful in art with all that was interesting in the remains of antiquity."







post a comment